
This is bad news for the companion star, which may be completely devoured by the pulsar. The pulsar siphons matter and momentum from its companion, gradually increasing the spin rate of the pulsar. Scientists think millisecond pulsars must have formed by stealing energy from a companion. In fact, millisecond pulsars require an additional source of energy to get going to such a high rotation rate. Pulsars are the size of small cities, so ramping them up to such high speeds is no small feat. (Bringing mass closer to the center of a spinning object increases its rotation speed, which is why figure skaters can spin faster by pulling their arms in toward their torso.) Pulsars spin because the stars from which they formed also rotate, and the collapse of the stellar material will naturally increase the pulsar's rotation speed. The fastest known pulsars can spin hundreds of times per second, and are known as fast pulsars or millisecond pulsars (because their spin period is measured in milliseconds). The slowest pulsars ever detected spin on the order of once per second, and these are typically called slow pulsars. Ozel also noted that the beam of radio waves emitted by a pulsar may not pass through the field of view of an Earth-based telescope, preventing astronomers from seeing it. Some neutron stars may have once radiated as pulsars, but no longer radiate (read more below). "For a neutron star to emit as a pulsar, it has to have the right combination of magnetic field strength and spin frequency," Ozel told in an email. While Earth has a magnetic field that's just strong enough to exert a gentle tug on a compass needle, pulsars have magnetic fields that range from 100 million times to 1 quadrillion (a million billion) times stronger than Earth's. Pulsars are neutron stars are also highly magnetic. Scientists don't know exactly how massive neutron stars can get before they become black holes, according Feryal Özel, a professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Arizona State University, who specializes in compact objects and extreme states of matter in the universe. The most massive neutron star ever measured is 2.04 times the mass of the sun. The only object with a higher density than a neutron star is a black hole, which also forms when a dying star collapses.

The gravitational pull on the surface of a neutron star would be about 1 billion times stronger than the gravitational pull on the surface of the Earth. A sugar-cube-size bit of material from a neutron star would weigh about 1 billion tons (0.9 metric tons) - "about the same as Mount Everest," according to NASA. Neutron stars are typically about 12.4 to 14.9 miles (20 to 24 kilometers) in diameter, but they can contain up to twice the mass of the sun, which is about 864,938 miles (1.392 million km) in diameter. The neutron star is the dense nugget of material left over after this explosive death. This stellar death typically creates a massive explosion called a supernova. Pulsars belong to a family of objects called neutron stars that form when a star more massive than the sun runs out of fuel in its core and collapses in on itself. Pulsars aren't really stars - or at least they aren't "living" stars.

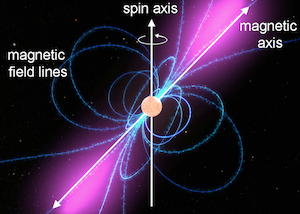
The fastest known millisecond pulsars can rotate more than 700 times per second. Most of those rotate on the order of once per second (these are sometimes called "slow pulsars"), while more than 200 pulsars that rotate hundreds of times per second (called "millisecond pulsars") have been found. Over 2,000 pulsars have been detected in total. (Image credit: NASA)īecause the "blinking" of a pulsar is caused by its spin, the rate of the pulses also reveals the rate at which the pulsar is spinning. The cone is not aligned with the spin axis, which is why the beam sweeps across the sky instead of pointing in just one direction. This diagram of a pulsar shows the yellow cone of light that can be seen by astronomers on Earth.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
